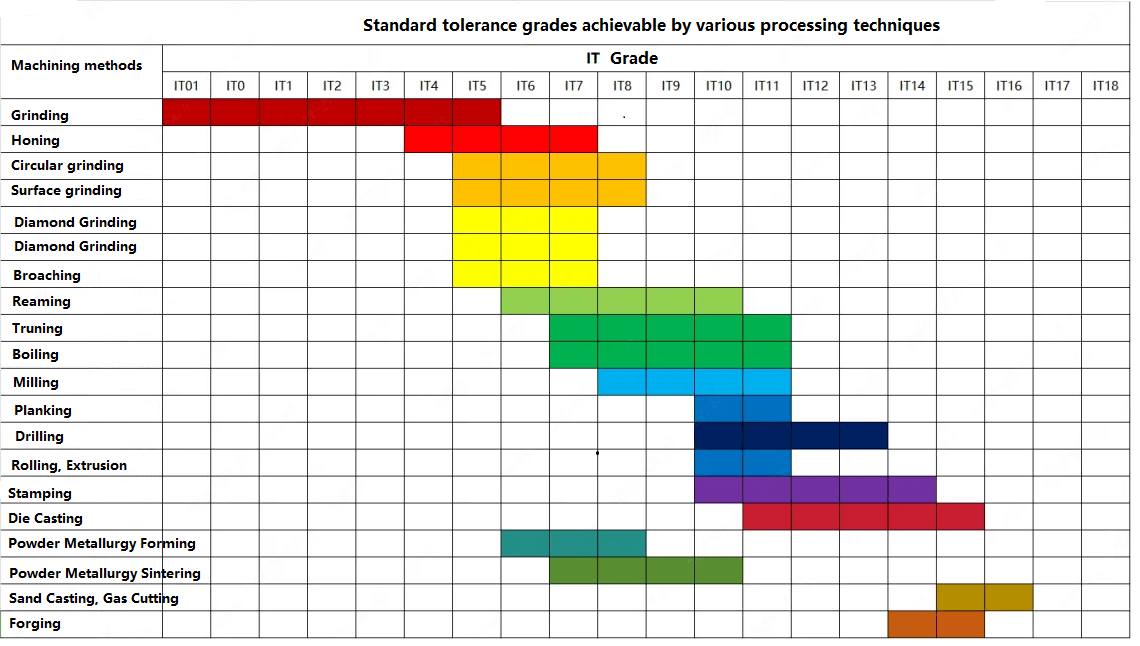
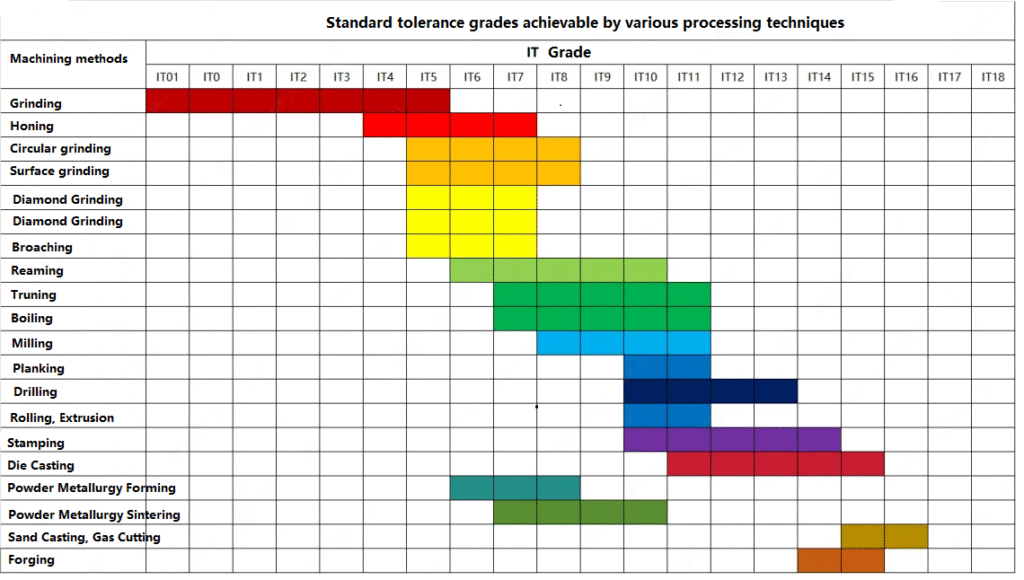
In CNC manufacturing, machining accuracy directly determines the quality and performance of a component. Different machining processes such as turning, milling, grinding, boring, drilling, and planing all have their own precision levels and tolerance ranges.
In this article, we’ll explore standard machining tolerances achieved by various CNC processes and help you understand how to choose the right machining method based on your accuracy requirements.
Table of Contents
Understanding Machining Accuracy and Tolerance Grades
Before comparing the precision ranges of different machining methods, let’s first understand what machining accuracy means.
Machining accuracy refers to how closely a manufactured part matches its design dimensions. The tolerance grade (IT grade) is the standard used to quantify machining accuracy, the smaller the grade number, the higher the accuracy.
| Precision grade & machining method | |||||
| Machining precision | Surface Features | Dimensional accuracy range | Ra value range (μm) | Corresponding machining methods | Common Applications |
| No machining | Clear burrs | IT16~IT14 | Castings, forgings, welded parts, stampings | ||
| Rough machining | Visible tool marks | IT13~10 | ≤80 | Rough turning, rough boring, rough milling, rough planing,drilling, rough filing, sawing, etc. | For non-mating dimensions or unimportant fits |
| Visible tool marks | IT10 | ≤40 | For general requirements, mainly for length fits | ||
| Slightly visible tool marks | IT10~IT8 | ≤20 | |||
| Semi-finishing | Visible machining marks | IT10~IT8 | ≤10 | Semi-finish turning, semi-finish boring, semi-finish milling, semi-finish planing, reaming, etc. | For important fits |
| Slightly visible machining marks | IT8~IT7 | ≤5 | Finish turning, finish boring, finish milling, finish planing, rough grinding, rough reaming, etc. | ||
| No machining marks | IT8~IT7 | ≤2.5 | |||
| Fine machining | Machinery mark direction identifiable | IT8~IT7 | ≤1.25 | Precision turning, precision planing, precision grinding, precision reaming, etc. | |
| Machinery mark direction slightly identifiable | IT7~IT6 | ≤0.63 | For precision fits | ||
| Machinery mark direction not identifiable | IT7~IT6 | ≤0.32 | |||
| Ultra-finishing | Dark gloss surface | IT6~IT5 | ≤0.16 | Fine grinding, lapping, mirror grinding, ultra-precision machining, polishing, etc. | Gauge blocks, measuring instruments, and precision meters; finishing of precision parts |
| Bright gloss surface | IT6~IT5 | ≤0.08 | |||
| Mirror gloss surface | IT5~IT2 | ≤0.04 | |||
| Hazy gloss | IT5~IT2 | ≤0.02 | |||
| Mirror finish | IT5~IT2 | ≤0.01 | |||
According to ISO and GB standards, tolerance grades are divided into 20 levels, ranging from IT01, IT0, IT1… up to IT18.
The smaller the IT grade number, the tighter the tolerance and the higher the machining precision.
The larger the IT grade number, the looser the tolerance and the lower the machining precision, but also the easier and cheaper the process.
For example:
IT01 represents ultra-high precision components.
IT18 represents parts with very low precision requirements.
Typical industrial machinery is often made to IT7, while agricultural machinery is usually IT8.
Tolerance Levels Achievable by Different Machining Methods
Product components require varying levels of machining precision based on their functional applications, necessitating different machining forms and processes. The table below outlines the precision ranges and standard tolerance grades achievable through various machining methods.
01 Turning Machining Accuracy
Turning machining typically achieves IT8 to IT7 accuracy with surface roughness Rα 1.6μm to 0.8μm. Specifically:
- Rough turning: Achieves only IT11 accuracy with surface roughness Rα 20 (10μm).
- Semi-finish and finish turning: Achieves IT10 to IT7 precision with surface roughness Rα10 (0.16μm).
- High-precision lathe machining: Reaches IT7 to IT5 precision with surface roughness Rα0.04 (0.01μm), also known as “mirror turning.”
02 Grinding Accuracy
Grinding is typically employed for semi-finishing and finishing operations, primarily focused on surface finish. It achieves machining accuracy of IT8 to IT5 or higher, with surface roughness Rα1.25 (0.16 μm).
- Precision Grinding: Surface roughness ranges from Ra 0.16 to 0.04 μm.
- Ultra-Precision Grinding: Surface roughness ranges from Ra 0.04 to 0.01 μm.
- Mirror Grinding: Surface roughness can achieve below Ra 0.01 μm.
| Machine tool type | |||||||
| Machine tool type | Roundness/mm | Cylindricity | Flatness (recessed) (by diameter) | ||||
| Conventional Lathe | Maximum machining diameter/mm | ≤400 | 0.01 | 0.0075/100 | 0.015/200 0.02/300 0.025/400 0.03/500 0.04/600 0.05/700 0.06/800 0.07/900 0.08/1000 | ||
| >400~800 | 0.015 | 0.025/300 | |||||
| >800~1600 | 0.02 | 0.03/300 | |||||
| >1600~3200 | 0.025 | 0.04/300 | |||||
| High-Precision Conventional Lathe | ≤500 | 0.005 | 0.01/150 | 0.01/200 | |||
| Cylindrical Grinding Machine | Maximum grinding diameter/mm | ≤200 | 0.003 | 0.0055/500 | – | ||
| >200~400 | 0.004 | 0.01/1000 | |||||
| >400~800 | 0.006 | Full length:0.015 | |||||
| Centerless Grinding Machine | 0.005 | 0.004/100 | The deviation of the equal-diameter polygon is 0.003. | ||||
| Honing Machine | 0.005 | 0.01/300 | – | ||||
| Machine tool type | Roundness/mm | Cylindricity | Flatness (recessed) (by diameter) | Dispersion of batch workpiece dimensions / mm | |||
| Longitude | Long straight | ||||||
| Hexagonal lathe | Maximum bar diameter / mm | ≤12 | 0.007 | 0.007/300 | 0.02/300 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
| >12~32 | 0.01 | 0.01/300 | 0.03/300 | 0.05 | 0.15 | ||
| >32~80 | 0.01 | 0.02/300 | 0.04/300 | 0.06 | 0.18 | ||
| >80 | 0.02 | 0.025/300 | 0.05/300 | 0.09 | 0.22 | ||
03 Drilling Machining Accuracy
Drilling achieves relatively low machining accuracy, typically reaching only IT10. Surface roughness generally measures Rα12.5, equivalent to 6.3μm.
Drilled holes often undergo reaming and boring for semi-finishing and finishing operations.
04 Boring Machining Accuracy
Boring is commonly employed between semi-rough and finishing operations.
For steel materials, boring precision generally achieves IT9 to IT7, with surface roughness of Ra 2.5–0.16 μm.
Precision boring can attain IT7 to IT6 accuracy, with surface roughness of Ra 0.63–0.08 μm.
| Machining Methods | Accuracy Class (IT) | Surface Roughness Ra/μm |
| Drill | 11~13 | 12.5 |
| Drill-Ream | 9~10 | 1.6~3.2 |
| Drill-Rough Ream-Fine Ream | 7~8 | 0.8~1.6 |
| Drill | 12~13 | 12.5 |
| Drill-Expand | 10~11 | 3.2~6.3 |
| Drill-Expand-Ream | 8~10 | 1.6~3.2 |
| Drill-Expand-Rough Ream-Fine Ream | 7~9 | 0.8~1.6 |
| Rough Boring | 11~13 | 6.3~12.5 |
| Rough Boring-Semi-Fine Boring | 9~11 | 1.6~3.2 |
| Rough Boring-Semi-Fine Boring-Fine Boring (Reaming) | 8~10 | 0.8~1.6 |
| Rough Boring-Semi-Fine Boring-Fine Boring-Floating Reaming | 6~7 | 0.4~0.8 |
05 Milling Machining Accuracy
Milling machining accuracy is generally IT8 to IT7, with a surface roughness of Ra 6.3, equivalent to 1.6 μm. Specifically:
- Rough milling: Machining accuracy IT11 to IT13, surface roughness Ra 5, equivalent to 20 μm.
- Semi-finish milling: Machining accuracy IT8–IT11, surface roughness Ra 2.5 μm (10 μm).
- Finish milling: Machining accuracy IT6–IT8, surface roughness Ra 0.63 μm (5 μm).
06 Planing Machining Accuracy
Planing machining accuracy is generally IT9~IT7, surface roughness Rα6.3, i.e., 1.6μm. Specifically:
- Rough planing: Machining accuracy IT12~IT11, surface roughness Rα25, i.e., 12.5μm.
- Semi-finishing planing: Machining accuracy IT10 to IT9, surface roughness Ra 6.2, equivalent to 3.2 μm.
- Finishing planing: Machining accuracy IT8 to IT7, surface roughness Ra 3.2, equivalent to 1.6 μm.
※ Select different machining methods based on varying precision requirements.
| Precision grade & machining method | |||||
| Machining precision | Surface Features | Dimensional accuracy range | Ra value range (μm) | Corresponding machining methods | Common Applications |
| No machining | Clear burrs | IT16~IT14 | Castings, forgings, welded parts, stampings | ||
| Rough machining | Visible tool marks | IT13~10 | ≤80 | Rough turning, rough boring, rough milling, rough planing,drilling, rough filing, sawing, etc. | For non-mating dimensions or unimportant fits |
| Visible tool marks | IT10 | ≤40 | For general requirements, mainly for length fits | ||
| Slightly visible tool marks | IT10~IT8 | ≤20 | |||
| Semi-finishing | Visible machining marks | IT10~IT8 | ≤10 | Semi-finish turning, semi-finish boring, semi-finish milling, semi-finish planing, reaming, etc. | For important fits |
| Slightly visible machining marks | IT8~IT7 | ≤5 | Finish turning, finish boring, finish milling, finish planing, rough grinding, rough reaming, etc. | ||
| No machining marks | IT8~IT7 | ≤2.5 | |||
| Fine machining | Machinery mark direction identifiable | IT8~IT7 | ≤1.25 | Precision turning, precision planing, precision grinding, precision reaming, etc. | |
| Machinery mark direction slightly identifiable | IT7~IT6 | ≤0.63 | For precision fits | ||
| Machinery mark direction not identifiable | IT7~IT6 | ≤0.32 | |||
| Ultra-finishing | Dark gloss surface | IT6~IT5 | ≤0.16 | Fine grinding, lapping, mirror grinding, ultra-precision machining, polishing, etc. | Gauge blocks, measuring instruments, and precision meters; finishing of precision parts |
| Bright gloss surface | IT6~IT5 | ≤0.08 | |||
| Mirror gloss surface | IT5~IT2 | ≤0.04 | |||
| Hazy gloss | IT5~IT2 | ≤0.02 | |||
| Mirror finish | IT5~IT2 | ≤0.01 | |||
Conclusion
Machining tolerance is the foundation of precision manufacturing. Knowing the capabilities of each CNC process from turning and milling to grinding and boring, helps you select the most efficient and cost-effective method for your part’s function and design requirements.
Whether you’re developing prototypes or high-volume production parts, mastering machining tolerances ensures consistent quality, proper fits, and long-term performance in every component.
YPMFG provides professional CNC machining services with tight tolerance control and surface finishing options. If you need precision custom parts, contact our machining experts to discuss your project requirements and achieve the ideal balance between accuracy, cost, and efficiency.